Top Cyber Security Threats
In the digital age, cybersecurity threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, posing significant risks to individuals and organizations alike. Understanding these threats is crucial for developing effective defenses. This blog will provide an overview of key cybersecurity threats and offer best practices for avoiding them.
-
Malware
Overview: Malware, short for malicious software, is designed to damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to systems. Common types include viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and spyware.
Impact: Malware can corrupt files, steal sensitive information, and render systems inoperable. Ransomware, in particular, encrypts files and demands a ransom for their release.
Best Practices:
- Install and regularly update antivirus software.
- Avoid downloading files from untrusted sources.
- Keep your operating system and software up to date with the latest patches.
-
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
Overview: A DoS attack overwhelms a system, server, or network with excessive traffic, causing it to become slow or entirely unavailable.
Impact: DoS attacks can disrupt business operations, leading to downtime and loss of revenue. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks involve multiple systems to amplify the attack.
Best Practices:
- Use network security solutions that include DDoS protection.
- Implement rate limiting and traffic filtering to manage and block excessive requests.
- Regularly test your infrastructure’s resilience to DoS attacks.
-
Man in the Middle (MitM) Attacks
Overview: In a MitM attack, an attacker intercepts and potentially alters communication between two parties without their knowledge.
Impact: MitM attacks can lead to data breaches, theft of sensitive information, and unauthorized access to accounts.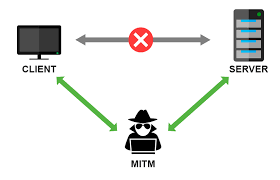
Best Practices:
- Use encryption protocols such as HTTPS for secure communications.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security.
- Be cautious when using public Wi-Fi; use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) for secure connections.
-
Phishing
Overview: Phishing involves tricking individuals into providing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details, by masquerading as a trustworthy entity.
Impact: Phishing can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and unauthorized access to systems and accounts.
Best Practices:
- Educate employees and users about recognizing phishing attempts.
- Verify the authenticity of emails and links before clicking.
- Use email filtering solutions to block phishing emails.
-
Brute Forcing
Overview: Brute force attacks involve systematically trying all possible combinations of passwords or encryption keys until the correct one is found.
Impact: Brute forcing can lead to unauthorized access to accounts and systems if strong passwords are not used.
Best Practices:
- Use strong, complex passwords that are difficult to guess.
- Implement account lockout mechanisms after a certain number of failed login attempts.
- Encourage the use of password managers to generate and store unique passwords.
-
SQL Injections
Overview: SQL injection attacks occur when an attacker inserts malicious SQL queries into input fields, allowing them to access and manipulate a database.
Impact: SQL injections can lead to unauthorized access to data, data corruption, and loss of data integrity.
Best Practices:
- Use parameterized queries and prepared statements to prevent SQL injection.
- Regularly update and patch database management systems.
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments.
-
Zero-Day Exploits
Overview: Zero-day exploits target vulnerabilities in software that are unknown to the vendor and for which no patch is available.
Impact: Zero-day attacks can be highly damaging as there are no immediate defenses or fixes available.
Best Practices:
- Keep all software and systems updated with the latest security patches.
- Implement intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) to identify and block suspicious activity.
- Monitor threat intelligence feeds for information on emerging vulnerabilities.
-
Botnets
Overview: Botnets consist of a network of compromised computers controlled by an attacker to perform coordinated tasks, such as launching DDoS attacks or spreading malware.
Impact: Botnets can be used to disrupt services, steal data, and spread malware on a large scale.
Best Practices:
- Regularly scan for and remove malware from your systems.
- Implement network monitoring to detect unusual traffic patterns.
- Use firewalls and intrusion prevention systems to block botnet traffic.
-
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Overview: XSS attacks involve injecting malicious scripts into webpages viewed by other users, enabling attackers to steal cookies, session tokens, or other sensitive data.
Impact: XSS can lead to data theft, account hijacking, and defacement of websites.
Best Practices:
- Sanitize and validate all user inputs to prevent script injection.
- Use Content Security Policy (CSP) headers to mitigate XSS risks.
- Regularly update and patch web applications to fix known vulnerabilities.
-
Rootkits
Overview: Rootkits are malicious software designed to gain and maintain unauthorized access to a computer while hiding their presence.
Impact: Rootkits can enable attackers to control a system remotely, evade detection, and modify system behavior.
Best Practices:
- Use reputable security tools that include rootkit detection capabilities.
- Regularly perform system scans and integrity checks.
- Ensure that all software and operating systems are updated with the latest security patches.
Avoiding Cyber Threats and Security Risks: Best Practices
To effectively mitigate cybersecurity risks, organizations and individuals should adhere to the following best practices:
- Implement Comprehensive Security Measures:
- Utilize firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems to protect against various types of attacks.
- Educate and Train Users:
- Conduct regular cybersecurity training to raise awareness about common threats and safe online practices.
- Regularly Update and Patch Systems:
- Keep all software, including operating systems and applications, up to date with the latest security patches.
- Use Strong Authentication Methods:
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance the security of user accounts.
- Backup Data Regularly:
- Regularly back up important data and ensure that backups are stored securely to prevent data loss in case of an attack.
- Monitor and Respond to Threats:
- Continuously monitor network activity for signs of suspicious behavior and have an incident response plan in place to address potential breaches promptly.
- Conduct Security Audits:
- Regularly perform security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential weaknesses in your security posture.
Conclusion:
In an increasingly connected world, the complexity and frequency of cybersecurity threats are escalating, making it essential to understand and address these risks effectively. From malware and phishing to sophisticated attacks like SQL injections and zero-day exploits, each threat poses unique challenges that can significantly impact individuals and organizations alike.
By familiarizing yourself with these common threats and implementing best practices—such as maintaining robust security measures, educating users, and regularly updating systems—you can enhance your ability to prevent, detect, and respond to potential cyber incidents.
Cybersecurity is not a one-time effort but a continuous process of vigilance and adaptation. As technology evolves and new threats emerge, staying informed and proactive is crucial for safeguarding your digital assets. Remember, a well-prepared and informed approach to cybersecurity can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to cyberattacks, ultimately leading to a more secure and resilient digital environment.
Should you encounter any of these threats, please do not hesitate to contact us for assistance.









